Korsis Otomasyon ve Bina Sistemleri
Potassium Based Aerosols
INTRODUCTION: It is time to talk about Potassium Based Aerosols, which are strengthened every day and shown as a new phenomenon in quenching technique.
When entering the subject, it is useful to look at the general problems of extinguishing agents. First of all, it is useful to specify the definitions related to the subject:
ODP: Ozone Depletion Potential; Ozone Depletion Potential. GWP: Global Warming Potential; Global Warming Potential.
Apart from these, the Toxic and Corrosive properties of extinguishing agents also affect their market status. As it is known, the only factor affecting the status of Halon Gas in the market was the ODP value (about 10 in Halon, 1 in Freon 13 gas). In those days, GWP was not on the agenda as a risk factor. Although the GWP value still does not affect the extinguisher market; global warming has now prevented the Ozone layer problem. In this context, the future of many gases that the major producers used as a marketing criterion in the past by using the ODP value creates a question mark.
For example; The GWP value of FM200, HFC227ea gases is 2900, and the FE 13 gas is 11700 (CO2 = 1) *.
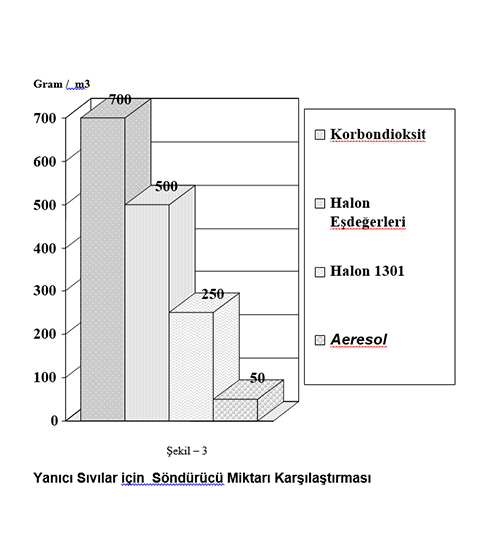
Currently, only inert gases such as CO2 *, argon, nitrogen have a GWP value of zero among the extinguishing gases commonly used in the market. However, the storage and pressure problems of these gases and the fact that they extinguish by affecting the oxygen percentage limit their situation in the market.
Potassium-based Aerosols, which have recently started to be seen in the market, attract attention with their zero ODP and GWP values, their lack of toxic and corrosive effects, and their quenching character close to Halon and emerge as a serious alternative.
* Although the GWP value of CO2 gas is 1, its contribution to global warming is considered to be zero since it is obtained from the atmosphere.
Potassium Based Aerosols
The history of Potassium Based Aerosols is actually not new on the basis of this sector. It is a product that was once developed by the Soviet Union as part of the Soyuz project. Normally, the extinguisher, which is kept unpressurized, is reacted by an activator to produce aerosol. It took part in Soyuz Projects and then moved to commercial applications mainly because it does not require a pressure vessel and it can quench large volumes very successfully with very small quantities.
The products currently on the market are either the know-how of the system used in the original Soyuz Project or the advanced versions developed from it.
Essentially, these aerosols perform the extinguishing function by breaking the Combustion Chain on the Fuel side. Potassium-based aerosols are the closest alternative to Halon with these aspects. (See figure-1)
As shown in Figure 1; 3 inputs are required for the burning event to occur:
• Fuel
Oxygen
• Heat
Disabling one of them breaks the combustion chain and the combustion ceases. Inert gases such as CO2, Argon, Nitrogen affect the oxygen concentration, gases such as HFC 227ea, FM200, FE25 with thermal decomposition, some extinguishers such as Halon, Potassium-based aerosol, break the combustion chain by affecting the combustion ability of fuels.
The substances required for the formation and spread of the combustion are O, OH, H. These are called fire-producing radicals or "Free Radicals". Potassium radicals (K) in Potassium Based Extinguishers mainly affect these free radicals:
K + OH = KOH
KOH + H = K + H2O